What you need to know about cataracts?
Cataracts cause more vision problems globally than any other eye condition or disease, and the number of cataracts is increasing with the aging population.
A cataract causes a part of the lens to becomes opaque, or cloudy. Light does not pass through easily, and vision becomes blurry, like looking through a fogged-up window. The cloudier the lens, the worse the vision will be.
Congenital cataracts may be present at birth or appear shortly after, or at some time during infancy or childhood.
Age-related cataracts appear later in life and are the most common type. This article will focus on age-related cataracts.
Cataract surgery is a routine operation nowadays and the most common kind of eye surgery.
Surgery
For severe cataracts, the only effective treatment is surgery.
The specialist will recommend surgery if the patient:
- Is having trouble looking after themselves or someone else
- Cannot drive or finds driving difficult
- Has problems leaving the house
- Finds it hard to see or recognize people’s faces
- Has problems doing their job
- Cannot read or watch television properly
Patients who take alpha-blockers or are considering taking alpha-blockers should be aware that these drugs may increase the difficulty of cataract surgery.
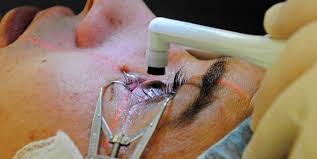
What to expect in surgery
As the anesthetic starts working, the area will become numb, and the patient will feel nothing. During the operation they will be aware of a bright light, but they will not be able to see what is happening. Cataract surgery is normally keyhole, or minimally invasive, surgery, and the patient will return home on the same day.
Various types of replacement lens may be used:
- A monofocal lens is a fixed-strength lens that is set for one level of vision, usually distance
- A multifocal lens may have two or more different strengths, providing for near and distance vision
- An accommodating lens is most similar to the natural human lens. It allows the eye to focus on near and distant objects
The operation involves removing the cloudy lens from the eye and putting an artificial, clear, plastic one in its place. This is an intraocular implant, or an intraocular lens.
This is known as phacoemulsification or phaco-extracapsular extraction.
The eye surgeon makes a tiny cut in the cornea at the front and inserts a minute probe through the cut. The probe uses ultrasound and breaks up the cloudy lens into very small pieces. These are sucked out.
The artificial lens is then inserted through the cut. The lens capsule acts as a pocket, to hold the lens in place. When it is first inserted the lens is folded, but it unfolds when in position.
The whole procedure takes around 30 minutes. Most patients will wear an eye pad for protection for a short while.
Symptoms
Cataracts normally take years to develop, and they tend to appear in older age. The lens gradually becomes cloudy.
Cataracts can make it hard to read or drive a car, especially during the night. Seeing people’s facial expressions can become difficult.
They develop slowly, so most people do not know they have them at first, but as the clouding progresses, the vision gradually gets worse. Long-distance vision is more severely affected at the beginning.
Cataracts often affect both eyes, but rarely equally.
People with cataracts may have the following symptoms:
- Blurry, cloudy, or misty vision
- Vision may be affected by small spots or dots
- The patient sees small patches that blur parts of the field of vision
- Vision worsens when lights are dim
- Vision is sometimes worse when there is very bright light, or glare
- Some people with cataracts also comment that colors appear less clear and faded
- Reading becomes difficult and eventually impossible
- Glasses need to be changed more frequently
- Eventually wearing glasses becomes less effective
- Rarely, the person may see a halo around bright objects, such as car headlights or street lights, or have double vision in one eye
As vision deteriorates, and the glare of oncoming headlights and street lights gets worse, driving becomes dangerous. Drivers with cataracts start to experience eyestrain and find themselves blinking more frequently as they try to clear their vision.
Cataracts do not usually change the appearance of the eye. Any discomfort such as irritation, aching, itching or redness is more likely caused by another eye disorder.
Cataracts are not hazardous to the health of the person or the eye. If the cataract becomes hypermature, or completely white, there may be inflammation, headache, and some pain. A hypermature cataract that causes pain or inflammation needs to be removed.
Dr. Birendra Jha is one of the best surgeons in Indore for Cataract surgery, who performs all types of treatment related to eyes under one roof such as Glaucoma, Pediatric Ophthalmology, Orbit and Oculoplasty, Comprehensive Eye Check Up, LASIK & Refractive Surgery, Cataract & Phaco Surgery / MICS and Squint/ (तिरछापन)/ Eye Deviation etc. If you are struggling with any type of problem of your eyes, then you should visit Indore India Eye Care Clinic Indore. Book an Appointment today visit on online website - http://www.indoreindiaeyecare.com/ and call us 9977141260.
Online Book an Appointment today :- https://www.indoreindiaeyecare.com/contact-us.html
Please go through our social media :
like our page to know more about eyes
Facebook :- https://www.facebook.com/eyeclinicsinIndore/
Please do follow on Instagram
Instagram :- https://www.instagram.com/indoreindiaeyecare_/
To More Post: - Types of Cataracts



Comments
Post a Comment